Address
304 North Cardinal St.
Dorchester Center, MA 02124
Work Hours
Monday to Friday: 7AM - 7PM
Weekend: 10AM - 5PM
Address
304 North Cardinal St.
Dorchester Center, MA 02124
Work Hours
Monday to Friday: 7AM - 7PM
Weekend: 10AM - 5PM

Security logs pile up fast, thousands of entries about who’s logging in, what files changed, and which systems are talking to each other. Making sense of it all? That’s where SIEM log management comes in.
It’s basically a big filter that sorts through the noise and points out what needs attention. MSSP teams can’t afford to miss important alerts while checking every single log entry manually.
Need a better way to handle your log headaches? Keep reading.
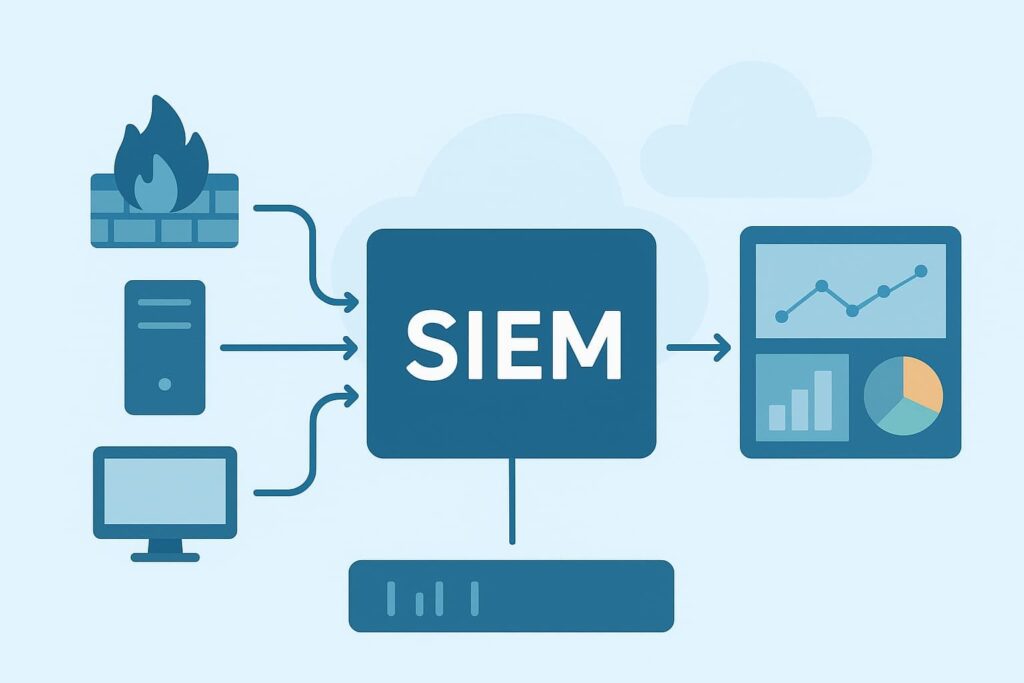
Most managed security providers struggle with the same challenge, making sense of endless log streams from dozens of client environments. The average MSSP juggles data from firewalls, cloud services, endpoints, and network gear across multiple platforms. We’ve spent years helping providers pick the right tools to handle this complexity.
The core of any solid SIEM setup starts with getting those logs in one place. Our audits show that many MSSPs try to cut corners here, but skipping proper log collection always comes back to bite them later. When providers come to us for help, this is usually where the trouble began.
A variety of methods come into play for gathering logs across client environments. Small consulting teams like ours frequently recommend a blend of agent-based solutions, which means putting lightweight collectors on endpoints and servers. These agents dig deep, they catch everything from failed login attempts to USB device connections.
Working with dozens of MSSPs, we’ve found that agentless collection through syslog and Windows Event Forwarding cuts down on maintenance headaches, especially in larger networks. The approach makes sense when dealing with thousands of endpoints. No software to update, no agents to manage.
Cloud environments need special attention. Most providers expose APIs that security teams can tap into directly. Amazon CloudWatch, Azure Monitor, and Google Cloud Logging provide raw data feeds, they’re gold mines for catching misconfigurations and access anomalies.
Getting log collection right matters more than ever. Through countless product audits, our team has seen the aftermath of partial coverage. An MSSP might monitor 98% of their infrastructure perfectly, but that remaining 2% gap frequently becomes the foothold attackers need. Complete visibility isn’t just a checkbox, it’s the foundation everything else builds on. [1]
Credit: IBM Technology
Raw logs from security tools look like alphabet soup, every vendor formats data differently, timestamps don’t match, and field names clash. Last month, an MSSP client struggled with 12 different time formats across their security stack. Their analysts wasted hours manually converting timestamps just to piece together what happened during an incident.
Most security teams know they need normalization, but the devil’s in the details. Our assessments regularly uncover parsing rules that miss critical data fields or mangle special characters.
Through hundreds of SIEM deployments, we’ve refined a process to extract the essentials: timestamps (normalized to UTC), source/destination IPs, usernames, event codes, and status flags.
Getting the structure right transforms investigation workflows. When timestamps line up and field names match, analysts can track an attack’s progression across multiple systems in minutes, not hours. During recent product evaluations, we’ve pushed vendors to demonstrate their parsing capabilities with real-world log samples, fancy demos with pristine data don’t cut it anymore.
The right normalization approach depends heavily on an MSSP’s tech stack and client requirements. Some teams need every field preserved for compliance, while others focus on extracting just security-relevant details. There’s no one-size-fits-all solution, but consistent structure remains non-negotiable for effective threat detection.
Storing logs securely and scalably is non-negotiable. Logs often contain sensitive information, so we implement encryption both at rest and in transit. Access controls ensure only authorized personnel can view or modify log data. Retention policies balance compliance obligations, like GDPR or HIPAA, with practical needs for forensic investigations.
Strong secure log storage analysis practices help maintain integrity and retrieval speed without exposing critical data.
This is where SIEM shines. Our systems apply rule-based correlation to flag known malicious sequences, multiple failed logins followed by a successful one, for example. But we don’t stop there; incorporating machine learning and behavioral analytics helps detect subtle anomalies that static rules might miss.
By integrating threat intelligence feeds, we enrich log data with context about known bad actors, improving detection accuracy.
A flood of alerts can overwhelm any security team. We configure alert thresholds carefully to minimize false positives, prioritizing alerts by severity. Notifications reach the right people through email, SMS, or integrated platforms, ensuring rapid awareness and action. [2]
We’ve found that automating response wherever possible, isolating infected endpoints, blocking suspicious IPs, or triggering workflows in orchestration tools, significantly reduces response times. Clear incident response plans guide the team through each step, supported by integration with SIEM alerts.
Regulatory compliance is a constant demand. SIEM integration supports generating detailed reports that satisfy auditors and internal policies alike. Teams that emphasize log management for compliance gain a clearer view of risk exposure while ensuring consistency across audits. Custom dashboards visualize security posture, recent incidents, and trending threats, enabling proactive management.
SIEM systems don’t operate in a vacuum. We connect them with threat intelligence platforms, intrusion detection systems (IDS), and other security tools to create a unified defense ecosystem, streamlining incident investigation and remediation.
From firsthand experience managing MSSP Security operations, we recommend these best practices:

Managing SIEM log management integration is not without hurdles:
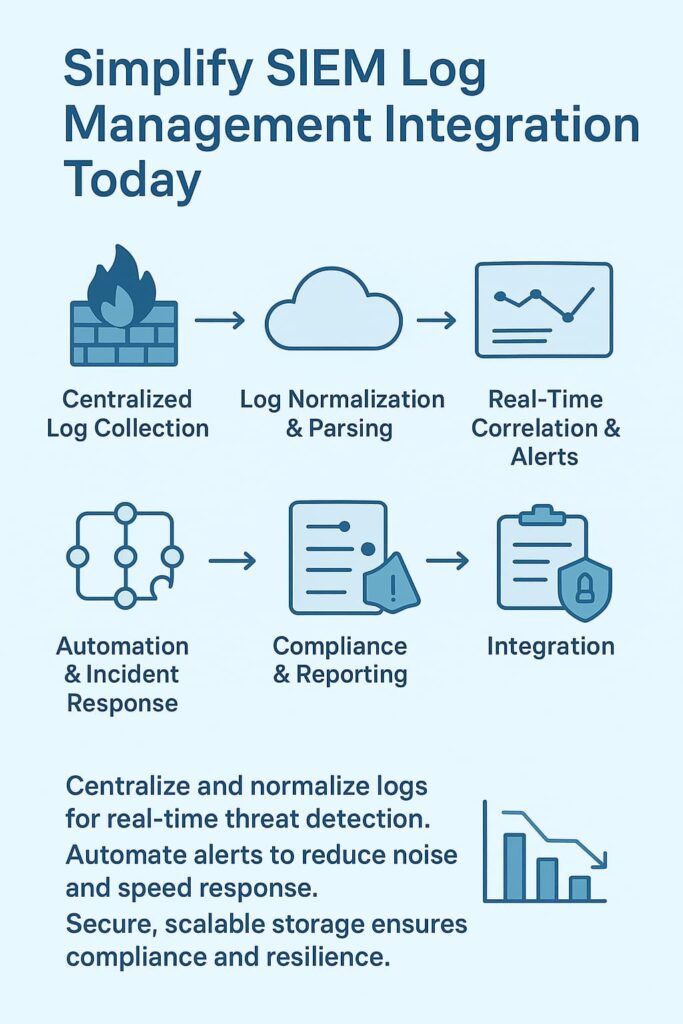
SIEM log management integration combines security information management and event management into one system.
It gathers data through log aggregation and log data ingestion from multiple sources, then applies log normalization and event correlation for real-time log analysis. This helps security teams detect threats faster and manage compliance reporting efficiently.
Centralized logging pulls together application logs, firewall logs, and network traffic logs into one dashboard. By using log parsing rules and log aggregation pipelines, analysts can easily spot patterns or anomalies. This setup powers automated threat detection and anomaly detection through UEBA integration and machine learning for logs.
Good log retention policies balance compliance reporting with performance. Using log storage tiers and log compression reduces cost while keeping encrypted log data safe. Many teams also use long-term log archiving with log integrity validation to maintain log audit trails for forensic log analysis and security event correlation.
Automation boosts SOC efficiency by handling alerting mechanisms and event triage. It connects log forwarding protocols, event enrichment, and telemetry data integration to streamline workflows.
Incident response automation and alert prioritization reduce noise so security operations centers can focus on high-risk events flagged by the data correlation engine.
The security landscape is evolving fast, and SIEM log management integration turns scattered data into real-time intelligence. At MSSP Security, we help teams detect threats earlier, automate responses, and simplify compliance through unified log visibility.
Our experts guide you in assessing log sources, optimizing retention, and building scalable, secure infrastructure.
Join MSSP Security to streamline your operations, cut tool sprawl, and strengthen service quality. With 15+ years of experience and 48K+ projects completed, we deliver vendor-neutral consulting, PoC support, and integration strategies that enhance efficiency, visibility, and resilience in every layer of your cybersecurity stack.