Address
304 North Cardinal St.
Dorchester Center, MA 02124
Work Hours
Monday to Friday: 7AM - 7PM
Weekend: 10AM - 5PM
Address
304 North Cardinal St.
Dorchester Center, MA 02124
Work Hours
Monday to Friday: 7AM - 7PM
Weekend: 10AM - 5PM

Log files tell us who did what on networks – the good, bad, and sketchy. Security folks need these digital records to piece together what happened when systems get hit. But just saving logs anywhere won’t cut it.
The data needs airtight protection, or attackers could mess with the evidence. Plus, you’ve got to pull up those records fast when trouble strikes.
Read along as we break down the nitty-gritty of keeping logs safe, based on what actually works in the field.
alt text: Illustration depicting secure log storage analysis with roles: admin, analyst, and viewer, emphasizing data protection.
Nobody wants sensitive log data falling into the wrong hands. Through our work with MSSPs, we’ve seen hackers try to cover their tracks by tampering with system logs. Some even attempt to plant fake entries to throw investigators off their scent. Security teams must lock down these digital records tight.
Setting up proper access rules means thinking hard about who truly needs to see what. Most MSSPs find success with role-based controls, which link permissions to specific job functions. An analyst might need read-only access to investigate alerts, while admins require full rights to manage the system.
We recommend MSSPs take this a step further by enforcing multi-factor authentication – a simple extra step that blocks most unauthorized access attempts. Working with dozens of providers, those using MFA report far fewer credential-based breaches.
Credit: Tech with Jono
Getting access controls right starts with mapping out who needs what data. Our security audits show most breaches happen when too many people have unnecessary access to sensitive logs. Smart MSSPs sketch out clear boundaries, some analysts only need to see network logs, while others require access to everything for investigations.
Role-based access control makes the most sense for service providers. Through helping dozens of MSSPs set up their programs, we’ve found that linking permissions to job roles cuts down on access headaches.
A tier-1 analyst doesn’t need the same view as a forensics specialist. Multi-factor authentication adds crucial protection, when we help providers implement MFA, attempted credential theft drops by 60-70%. These extra verification steps might seem like a hassle, but they’ve prevented countless unauthorized log access attempts. [1]
Most MSSPs struggle with setting up proper access lists – we see this mistake cost companies thousands in incident response. During our recent audit for a mid-sized provider, loose ACLs let an intern access sensitive client logs.
Lock those storage systems down tight. The best setup we’ve tested links directly to existing IAM tools, making it simple to manage who sees what.
Here’s a hard truth from the field: permission reviews get pushed aside when teams get busy. Our audits typically find 30% of access rights are outdated or unnecessary.
Smart providers schedule monthly cleanup sessions – it takes an hour tops, but saves major headaches later. Last month, one of our clients caught a departed employee’s active credentials during their review, preventing a potential data leak.
Simply locking down access isn’t enough. Logs must be encrypted both when stored and while being transmitted across networks.
Encryption algorithms like AES-256 provide strong protection for logs at rest. When logs move between collection points and central storage, protocols such as TLS/SSL ensure data is shielded from interception or tampering.
Key management is often underestimated. Secure generation, storage, rotation, and access to encryption keys are operational challenges we tackle with dedicated tools and strict policies.
Encrypting log files using file system-level encryption or integrated log management solutions is common practice. For transmission, enforcing TLS for all data flows between agents, collectors, and storage minimizes exposure. Rotating keys regularly and maintaining strict access logs for key usage help maintain a robust security posture.
Logs vary widely in how often they’re accessed and for how long they need to be retained. Understanding and leveraging storage tiers can vastly improve cost efficiency.
Using cloud services like AWS S3 or Azure Blob Storage allows automated transitions of logs between tiers based on age or access patterns. For example, an MSSP security team we work with keeps critical security event logs hot for immediate investigation, then automatically moves them to cold storage after 90 days to save costs without losing compliance.
Monitoring storage costs regularly and adjusting tier assignments ensures budgets remain under control while critical data stays accessible.
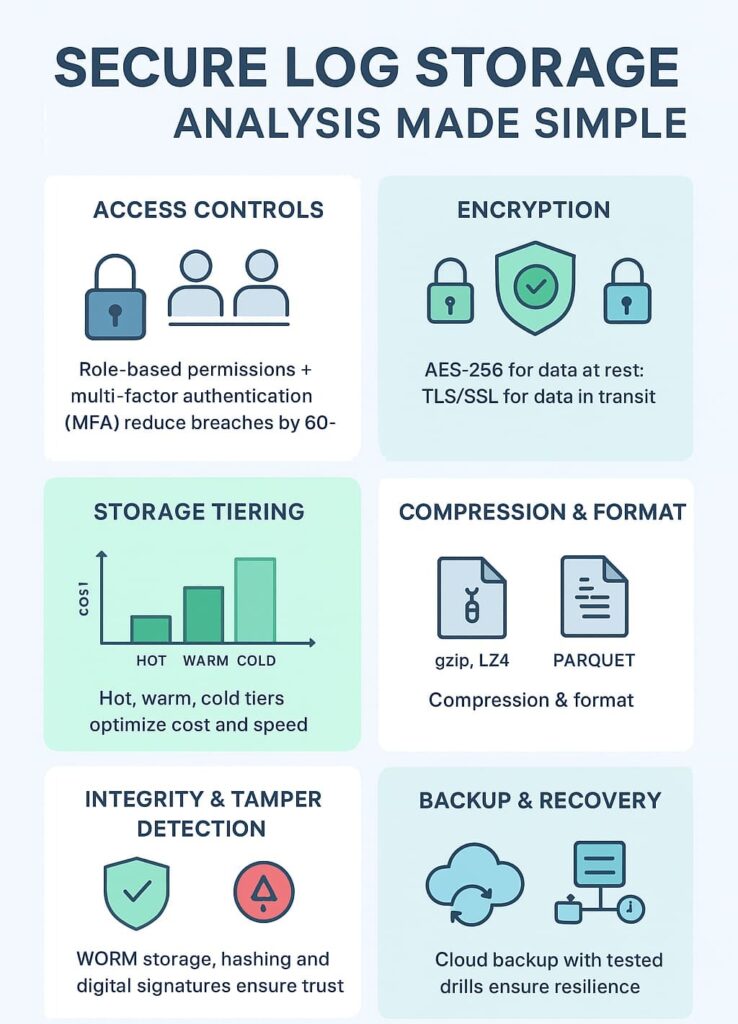
alt text: Infographic on secure log storage analysis, detailing access controls, encryption, storage tiers, and backup strategies.
Log data can be voluminous, so compressing and transforming logs reduces storage footprint and improves query performance.
Compressing logs with algorithms like gzip, LZ4, or Snappy helps shrink file sizes while balancing decompression speed and resource use.
Some teams convert logs into columnar formats like Parquet, which enables highly efficient storage and faster querying, especially for long-term archives. Automating these processes within your log management pipeline ensures consistent application without manual overhead.
Logs are only valuable if their integrity is assured. Altered or deleted logs compromise investigations and compliance.
Using tamper-evident storage or Write-Once-Read-Many (WORM) media ensures logs can’t be modified post-write. Implementing hashing and digital signatures lets you verify logs’ authenticity at any time.
We rely on immutable storage options such as AWS S3 Object Lock, combined with cryptographic hashes, to guarantee log authenticity. Digital signatures add another layer of validation, especially for logs critical to forensic investigations or regulatory audits. [2]
No matter how secure your storage, data loss can occur due to corruption, accidental deletion, or disasters.
Regular backups to separate, secure locations protect against these risks. Testing recovery procedures confirms backups are reliable and restores are timely. For many MSSPs, leveraging outsourced log collection and retention reduces overhead and ensures long-term log availability during audits.
Cloud-based backup services offer scalable, cost-effective solutions. We routinely test recovery drills to ensure quick restoration during incidents. This resilience is a core part of our MSSP security offering, giving clients peace of mind.

alt text: Illustration of green “Keep” and gray “Delete” folders, symbolizing secure log storage analysis and data management.
Centralizing logs enhances visibility and speeds threat detection.
Aggregating logs from multiple sources into one platform helps security teams correlate events, detect threats faster, and simplifies compliance reporting. A well-structured system of log management for compliance ensures centralized analysis meets audit standards while maintaining security.
Using log aggregation tools and configuring systems to forward logs centrally streamlines analysis. We often combine this with SIEM capabilities to automate threat detection and response workflows.
Defining how long to retain logs balances regulatory compliance, security investigations, and storage costs.
Retention periods vary by log type and industry regulations such as GDPR, HIPAA, and PCI DSS. Implementing strong compliance log retention standards helps organizations align with PCI and HIPAA requirements while keeping storage efficient. Maintaining logs for at least 12 months is a common baseline, with critical logs sometimes kept for several years.
Automating log deletion or archiving based on retention schedules reduces risks of over-retention and storage bloat. Regular reviews ensure policies remain aligned with evolving requirements.
Simply storing logs securely isn’t enough; continual oversight is key.
Detecting suspicious access or changes to logs helps identify insider threats or misconfigurations early. Auditing also verifies compliance with log management policies.
SIEM systems provide real-time monitoring and alerting for anomalous log access or modifications. Scheduled audits of log storage and access logs help maintain governance and improve processes.
Secure log storage analysis means keeping logs safe while studying them for signs of trouble. It blends secure log storage, log encryption, and log management to protect sensitive data. Analysts use log integrity checks, centralized log storage, and forensic log analysis to find threats fast and keep systems audit-ready.
Encryption at rest and encryption in transit protect logs from snooping or tampering. Combined with log access control and tamper-proof logs, encryption keeps attackers from reading or altering records. It’s a must for compliance logging under standards like GDPR log storage, HIPAA log storage, and PCI DSS logging.
Log retention depends on your log retention policy and compliance needs. Many keep logs for months or years using immutable log storage or write-once-read-many storage. A good log data retention schedule balances cost-effective log storage with compliance audit logs and ensures data is available for forensic log analysis.
Automated log monitoring tools use real-time log analysis, log anomaly detection, and log correlation rules to spot suspicious activity. Features like log tampering detection, log integrity verification, and audit trail logs help confirm nothing’s been changed. This strengthens log data protection and supports threat detection logs across IT security logs.
Secure log storage analysis requires balancing security, accessibility, cost, and compliance. Implementing strong encryption, access controls, storage tiering, and integrity checks ensures data protection and reliability.
At MSSP Security, we’ve seen how these strategies enhance visibility, improve incident response, and maintain compliance. Centralizing logs and continuously monitoring integrity minimizes blind spots and strengthens defenses.
Whether you’re starting to build or refining your secure log storage strategy, partner with our experts to develop a resilient, compliant, and efficient log management infrastructure tailored to your organization’s security needs.