Address
304 North Cardinal St.
Dorchester Center, MA 02124
Work Hours
Monday to Friday: 7AM - 7PM
Weekend: 10AM - 5PM
Address
304 North Cardinal St.
Dorchester Center, MA 02124
Work Hours
Monday to Friday: 7AM - 7PM
Weekend: 10AM - 5PM

Vulnerability remediation at managed security firms means getting hands dirty with the boring but crucial task of finding and fixing system weaknesses. While some might think it’s just about running scanners and pushing patches, there’s way more going on behind the scenes.
The real work starts with a tedious inventory of every single device and app (yes, even that ancient printer in accounting that everyone forgot about). These security teams basically act like digital janitors, methodically sweeping through networks looking for holes to plug. They can’t just patch blindly either, each fix needs testing so nothing breaks in production.
The whole process requires careful planning, especially when dealing with cranky legacy systems that don’t play nice with updates. Want to know how the pros handle this mess? Keep reading.
Finding every device on a network’s kinda like playing digital hide and seek, there’s always something tucked away in a corner somewhere. Most clients swear they know what’s on their network, but then we find that one Windows XP box still humming away in the warehouse. So yeah, first thing’s first: we dig through everything. Physical servers, cloud stuff, those tablets everyone forgot about. All of it goes in the inventory.
Next comes the scanning part. We use tools like Nessus or Qualys (they’re pretty good at finding the obvious stuff), but machines miss things sometimes. A well-structured vulnerability management services guide helps ensure the process covers everything from initial discovery to remediation tracking.
Had a scanner once flag an entire subnet as vulnerable when it was just a misconfigured switch. That’s why we double-check everything, computers are fast but kind of dumb sometimes.
Once we know what’s broken, we gotta figure out what actually matters. Sure, CVSS scores help, anything above 9.0 probably needs fixing yesterday. [1] But numbers don’t tell the whole story. Like, a critical vulnerability in your payment system? That’s way more important than some medium risk in the break room printer.
We look at three main things: how bad is it (CVSS), how easy is it to hack (some stuff just needs a web browser), and what breaks if someone does hack it. Nobody’s got time or money to fix everything at once, so we focus on the scary stuff first.
Most days that means tackling the high-risk holes where hackers are already poking around. Everything else gets tracked and handled when it makes sense. Keeps everyone sane and focused on what really matters.
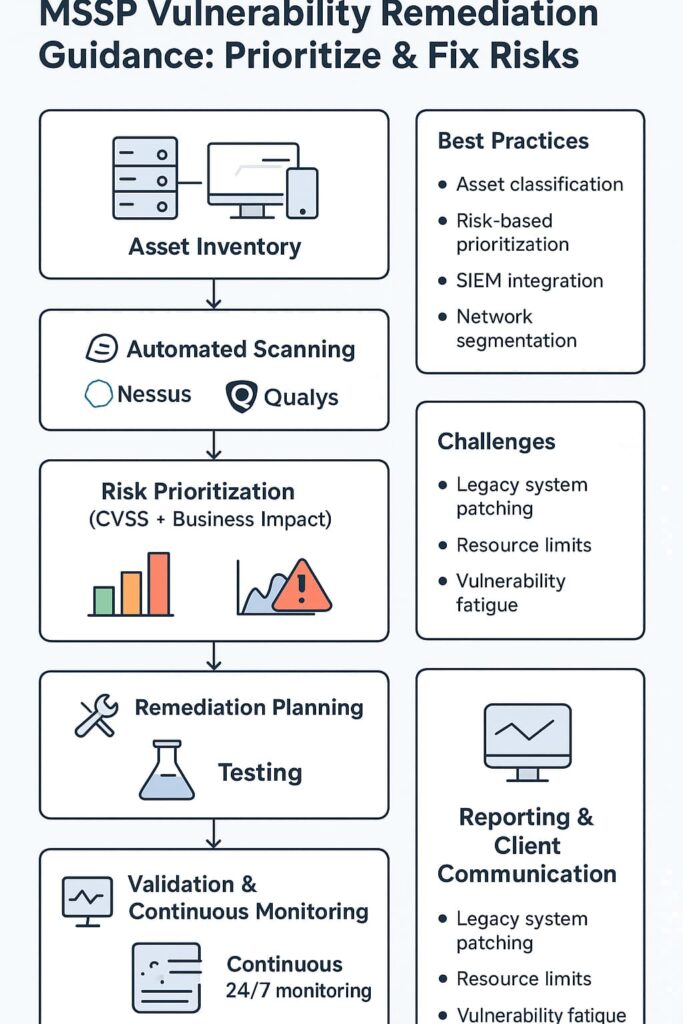
Nobody likes surprises in IT, especially when you’re trying to patch stuff. That’s why we sit down with clients and figure out what works for them. Some places can’t handle downtime during business hours (looking at you, e-commerce), while others need everything done by yesterday. Working out these details upfront saves everyone headaches later. [2]
There’s more than one way to plug a security hole. Sometimes it’s as simple as running Windows Update, but other times you gotta get creative:
Learned this one the hard way, always test patches in staging first. Had a client once whose entire inventory system crashed because of an untested security update. Not fun explaining that one to the boss. We’ve got a pretty solid setup now where we run everything through test environments first.

Fix something, check it worked. Simple right? Well, kinda. We go back through with scanners to make sure those vulnerabilities are really gone. Sometimes they hide, like that one time a patch looked successful but the service never actually restarted.
Networks change faster than most people change their socks. New stuff gets added, configurations drift, and fresh vulnerabilities pop up daily. That’s why a continuous vulnerability assessment service is essential, with monitoring tools running 24/7 and threat feeds keeping us ahead of the curve.
The SIEM system (fancy term for our log collector) helps connect the dots between what’s happening on the network and what the vulnerability scanners are yelling about. Makes it easier to figure out which fires to put out first.

Transparency is critical in MSSP relationships. We provide clients with detailed reports covering:
Regular updates keep clients informed and support compliance audits. Clear communication about remediation timelines and service tiers also sets expectations realistically.
Documenting each step from discovery through remediation supports audits and handovers, reinforcing accountability.
Effective vulnerability remediation doesn’t operate in isolation. We encourage collaboration between IT, security teams, and clients to embed remediation within a wider risk management framework. This includes incident response planning and change management.
Regular audits and client feedback sessions help us refine processes continuously. This cycle of improvement leverages technology advancements and operational lessons to reduce vulnerability exposure over time.
Credits: Red Sentry
Our vulnerability scanning arsenal typically includes Nessus, Qualys, or Rapid7. These tools automate discovery and provide comprehensive coverage. Patch management solutions streamline the update process, minimizing manual effort.
Threat intelligence platforms and SIEM integration add valuable layers of context, allowing us to prioritize vulnerabilities based on current attack trends.
Best practices such as network segmentation isolate critical assets, limiting blast radius during remediation. We also maintain detailed documentation to support audit trails and compliance.
Tracking remediation performance via key metrics, like MTTR, drives efficiency. Automation plays a growing role in scanning, prioritization, and reporting, helping overcome resource constraints.
The toughest part isn’t finding vulnerabilities but fixing them quickly enough. Many breaches happen because known patches linger uninstalled. We address this by automating as much of the remediation workflow as possible, cutting down the time from detection to resolution.
Resource limits often slow things down, which is why many providers leverage the benefits of outsourced vulnerability scanning to extend their coverage. Clear, client-centric service models then define response times and coverage levels, with multi-tiered options that help set realistic expectations.
Incorporating client input and continuously upgrading technology form part of our strategy to improve vulnerability management over time.
Many managed security service providers face vulnerability fatigue when teams get overwhelmed by continuous vulnerability alerts and scanning results. A solid vulnerability management strategy uses automated updates, proper scanning frequency, and false positive reduction to cut unnecessary noise.
By integrating SIEM integration and central logging, MSSPs can prioritize high CVSS score threats and focus on true vulnerabilities. This improves incident escalation, risk mitigation, and overall security posture while keeping client reporting clear and actionable.
Asset classification is key to vulnerability prioritization because not every device has the same risk tolerance. MSSPs should maintain an accurate asset inventory to guide patch deployment, secure configuration, and vulnerability testing. Grouping assets by importance helps with remediation timeline planning and supports compensating controls for legacy systems.
Combining threat intelligence and vulnerability database data allows for better policy enforcement, remediation compliance tracking, and incident response preparation. This approach streamlines remediation workflow and reduces vulnerability exposure.
MSSPs must perform remediation validation and remediation verification after security patching or configuration changes. Patch verification and vulnerability tracking ensure that vulnerability exposure has been reduced.
A remediation audit with clear remediation metrics like mean time to remediate helps measure success. MSSPs can use vulnerability scanners and security analytics to confirm results and meet service level agreements. Continuous monitoring and notification workflows help maintain cyber hygiene and detect issues before they escalate.
Patch management often conflicts with change management when deploying urgent security patches. MSSPs must set a remediation policy and create a remediation plan that respects regulatory requirements while minimizing downtime. Remediation ticketing systems and exception management workflows track patch deployment progress and allow vulnerability escalation when needed.
Using automated remediation and patch verification helps reduce manual errors, while vendor risk management ensures third-party software stays secure. This process improves vulnerability lifecycle management and compliance auditing.
Multi-tenancy security adds complexity to vulnerability detection and remediation compliance. MSSPs need clear user roles, credential management, and access controls to protect client environments. Network segmentation and endpoint protection reduce attack surface reduction risks.
MSSP tools like security automation and remediation ticketing help manage vulnerability escalation across different organizations. Client reporting should reflect each customer’s risk assessment, regulatory requirements, and remediation timeline. This structure improves vulnerability reporting and keeps remediation workflow organized and efficient.
Vulnerability remediation is a continuous process that starts with asset discovery and scanning, then moves to risk-based prioritization and carefully tested fixes. With clear communication and the right tools, MSSPs can reduce exposure time, stay compliant, and keep networks resilient in today’s shifting threat landscape.
Take the next step toward smarter vulnerability management. Join our MSSP consulting program to streamline operations, optimize your tech stack, and boost service quality with expert, vendor-neutral guidance.