Address
304 North Cardinal St.
Dorchester Center, MA 02124
Work Hours
Monday to Friday: 7AM - 7PM
Weekend: 10AM - 5PM
Address
304 North Cardinal St.
Dorchester Center, MA 02124
Work Hours
Monday to Friday: 7AM - 7PM
Weekend: 10AM - 5PM

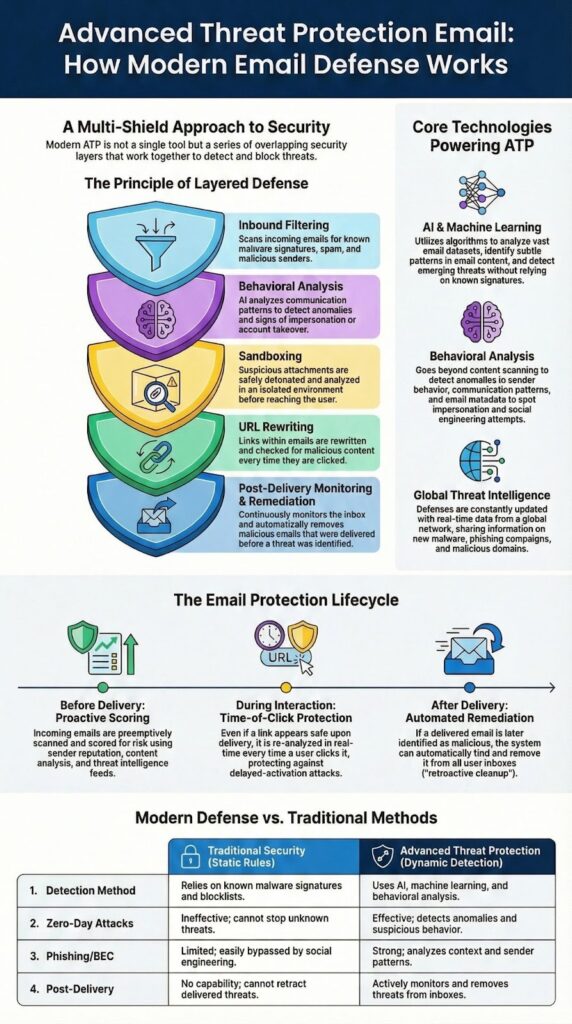
Email remains the most abused attack surface in business. Advanced threat protection email security exists because basic spam filters stopped being enough years ago. Attackers adapted. We had to as well. Advanced threat protection for email is not a single feature or switch.
It is a layered security architecture designed to detect, analyze, and respond to sophisticated email-borne threats before and after they reach inboxes. Keep reading to understand how modern email ATP really works, where traditional defenses fail, and why architecture matters more than tools.
Advanced threat protection focuses on context, not just content. It looks at:
In our audits for MSSPs, we see ATP tools flag spear phishing, executive impersonation, vendor fraud, and ransomware setups that all look routine on the surface. Often there’s no attachment at all, just urgency, trust, and a domain off by one character.
Unlike legacy gateways, ATP doesn’t stop at delivery. Strong platforms keep checking links at time of click, react to new threat intelligence, and can retroactively quarantine a message days later. We test that behavior directly when helping MSSPs choose products [1].
Traditional tools lean on signatures, blocklists, and static rules. Modern attackers use real accounts and clean cloud services instead. That’s why we look for:
Our work with MSSPs keeps confirming the same pattern: the quieter the attack, the more you need behavior‑driven email ATP.

We’ve seen over and over that “email ATP” works best when treated as an architecture, not a checkbox. The stronger MSSP environments we work with all share that same pattern.
Advanced threat protection stretches across the full flow of email:
No single layer catches everything, so each control is there to cover the others. When we help MSSPs design or audit these stacks, we assume failure somewhere, a user will click, an account will be taken over. The goal is fast detection and tight blast radius, not fantasy “perfect prevention.”
Most organizations now use cloud-based filtering with Microsoft 365 or Google Workspace. Some still add a secure email gateway in front. Native tools like Office 365 ATP, Exchange Online Protection, and Google’s controls give a baseline, but we consistently see gaps around business email compromise and account takeover.
That’s where layered, next-gen ATP and managed email security gateway deployments come in. The better service models combine native controls, external analysis, and active response to reduce dwell time and contain business email compromise faster. In our reviews with MSSPs, this mix is what actually cuts dwell time.
Strong ATP follows the email lifecycle:
Attackers often delay activation, so protection has to keep working long after the email lands.

Real ATP relies on several layers that cover each other. When we audit tools for our MSSP clients, we focus on how those layers behave together under real attack patterns.
Strong platforms start by breaking down the message and the sender:
We often review attacks where SPF, DKIM, and DMARC all pass. On paper, everything looks fine, but the email is still fraudulent. So domain spoofing protection alone doesn’t cut it.
Machine learning filters add another lens by scoring:
We feed real BEC examples into engines and watch whether they recognize that the message doesn’t match the sender’s usual style.
Modern attachment controls:
Suspicious files go to sandboxing, where behavior is watched instead of signatures, which is crucial for zero‑day threats.
For links, URL rewriting and time‑of‑click checks stop delayed weaponization, a pattern we still see driving ransomware‑style campaigns.
For MSSPs, the real value in email ATP shows up when tools can handle low‑signal attacks that look routine on the surface.
Stronger platforms pull threat intelligence from global telemetry, including:
When one organization gets hit, another can be protected shortly after because those indicators roll into the shared feed. In our product audits, we’ve seen exposure windows shrink when tools actually use these feeds well.
Behavioral engines learn normal communication patterns:
An anomaly, like a 3 a.m. wire request from a “vendor” who never emails at night, gets flagged. Business email compromise protection depends heavily on this context, and we test that with real case samples.
Modern models score hundreds of features: tone, domain similarity, logos, even QR codes. We’ve watched these systems improve over time as attackers change templates, especially around whaling and executive impersonation, where messages look polished but behavior doesn’t quite fit [2].
Credits : Microsoft Mechanics
Advanced email protection keeps working after messages leave the inbox, especially when users send data out or when a compromised account starts behaving strangely.
DLP for email watches outbound traffic for:
Policies can:
In our audits with MSSPs, this has stopped both accidental sends and deliberate exfiltration from hijacked accounts.
Encryption pairs well with ATP. Sensitive content can be encrypted automatically based on:
Access controls can restrict forwarding, downloading, or set expiry. We’ve seen this limit damage even when attackers gain mailbox access.
Core controls like DMARC, SPF, and DKIM are still foundational, but they’re not enough alone. Strong vendor compromise and spoofing defense also includes:
Real ATP value shows up in how fast a platform can move after it decides an email is bad, especially when remediation workflows are part of broader advanced specialized services that coordinate detection, cleanup, and response across multiple client environments.
The better tools we review for MSSPs don’t stop at raising an alert. They can:
We’ve watched organizations cut dwell time from hours to minutes once this is enabled, which changes the outcome of many incidents.
For incident response, we look for clear visibility into:
User reporting from the inbox is also valuable. Those “report phishing” clicks feed back into detection models and quietly support awareness training.
Email attacks usually touch other systems, so integration matters. Strong platforms connect to:
For MSSPs, that coordination turns email ATP into part of a larger, workable response system.
Advanced threat protection email goes beyond blocking spam by detecting sophisticated attacks. It uses advanced email threat protection, real time email scanning, and behavioral analysis email security to identify phishing, ransomware, and zero day email threat protection. This layered email defense blocks malicious attachments, unsafe links, and impersonation attempts before they reach user inboxes.
Email ATP security prevents phishing and business email compromise by analyzing sender identity, message behavior, and domain signals. It combines phishing email protection, spear phishing defense, and business email compromise protection. These methods detect email impersonation, display name spoofing, and domain spoofing attempts that often lead to invoice fraud and payment fraud.
Email sandboxing tests attachments in an isolated environment to detect hidden threats. It supports malicious attachment protection, attachment sandbox analysis, and advanced malware detection email. This process identifies ransomware email protection risks, PDF malware detection email issues, and office macro malware protection threats before users open infected files.
Safe email links protect users by checking URLs at the moment they are clicked. URL rewriting email security and time of click protection block access if a link later becomes malicious. This approach strengthens zero day email threat protection and reduces risk from delayed phishing campaigns and targeted email attack protection.
AI powered email security improves accuracy by using machine learning email filtering and anomaly detection email. It analyzes patterns across inbound email filtering, account takeover protection email, and compromised mailbox detection. This enables automated email remediation, retroactive email cleanup, and consistent enterprise email protection without relying on static rules.
Advanced threat protection for email works best when you treat it as a strategic control, not a one-time upgrade.
Attacks will keep coming. Techniques will change. The organizations that adapt fastest limit damage and recover with the least disruption. Modern email ATP supports that adaptability by combining:
On its own, ATP is just another dashboard. When it’s backed by experienced monitoring, tuning, and response, it becomes a core part of how an MSSP actually protects clients day to day.
If you want help turning email ATP into a reliable, high‑impact control across your MSSP services, you can work with a vendor‑neutral specialist team that focuses on:
Talk with our consulting team to align your ATP and security stack with your business goals and operational maturity.