Address
304 North Cardinal St.
Dorchester Center, MA 02124
Work Hours
Monday to Friday: 7AM - 7PM
Weekend: 10AM - 5PM
Address
304 North Cardinal St.
Dorchester Center, MA 02124
Work Hours
Monday to Friday: 7AM - 7PM
Weekend: 10AM - 5PM

OT security monitoring helps keep power plants, factories, and water systems safe by finding problems early. It also helps companies follow safety and legal requirements.
Ransomware attacks on important systems went up 34% in 2025, with factories seeing a 61% rise. As threats like hacking and insider misuse grow, OT security monitoring is now needed every day.
This guide shows how monitoring works, how it keeps systems safe, and how the right services help avoid downtime and rule issues. Keep reading to see how security can align with operational reality.

OT security monitoring watches industrial systems in real time to catch threats and unusual activity early. The U.S. market has grown to $4.64 billion as attacks on factories and energy companies increase.
Many industrial systems use older equipment that was not designed for cybersecurity. Modern monitoring tools keep an eye on systems and warn teams when something risky happens. Experts say cyber attacks now affect both safety and money at the same time.
OT security monitoring keeps important systems safe by finding problems early. In 2025, studies showed that 65% of organizations with managed OT monitoring solved problems faster than others.
This capability helps organizations:
Core monitoring outcomes include the following benefits:
These results help organizations prevent problems early without stopping important systems.
Managed services bridge the OT talent gap by providing 24/7 specialized services for protocol analysis, threat detection, and response. This takes the workload off small internal teams while keeping operations safe.
These services safely watch systems and look for unusual activity in industrial networks. OT-focused platforms specialize in traffic analysis without active scanning that could disrupt processes.
In 2025, many companies used managed OT services because about 70% of their older systems were out of date. These services watch systems and respond to threats quickly and effectively.
Organizations turn to managed OT monitoring to:
A managed OT security monitoring service typically includes these capabilities:
These services allow you to focus on uptime while experts manage exposure.

Protecting industrial control systems needs strong security at many levels to keep them safe and running, even if they are old.
ICS protection must prioritize ‘Resilience over Prevention’, focusing on rapid recovery and zoning, without introducing downtime or instability.
In 2025, audits showed that many older industrial systems were not secure because their software was old and passwords were weak.
PLC vulnerability scanning, when passive, helps identify exposure without interrupting operations. Read-only techniques support vulnerability management ICS without operational risk.
ICS security uses network separation, firewalls, and gateways to limit access and movement. Modbus and DNP3 security help stop unauthorized commands that could change how machines or systems work.
The Cybersecurity and Infrastructure Security Agency recommends using strong security to protect controllers.
Key control areas include:
Effective ICS protection blends policy and technology:
This approach reduces risk while maintaining production stability.
Seeing OT network traffic lets you clearly see devices, how they talk, and what they’re doing in real time across industrial networks. Without this visibility, attackers move laterally unnoticed.
About 31% of organizations still do not have a clear list of active remote access points, which makes it easier for attackers to hide. Passive monitoring tools watch all devices and learn what normal behavior looks like from network traffic.
OT traffic analysis decodes proprietary protocols and correlates events with process context. This enables teams to distinguish between routine maintenance and malicious actions.
Manufacturing cybersecurity programs increasingly depend on visibility to support insurance and regulatory expectations.
Visibility improves daily operations as well as security:
Clear visibility transforms OT networks from opaque to manageable.
| Capability | What It Provides | Why It Matters |
| Asset Discovery | Identifies all OT devices, including unknown and legacy assets | Eliminates blind spots and supports inventory accuracy |
| Protocol Analysis | Decodes OT protocols like Modbus, DNP3, and Profinet | Enables detection of unsafe or unauthorized commands |
| Behavioral Baselining | Learns normal traffic patterns | Allows fast detection of anomalies and attacks |
| Context Correlation | Links network activity to process operations | Helps distinguish maintenance from malicious behavior |

Finding OT threats focuses on unusual behavior in industrial systems, not just regular IT malware. Examples include PLC logic manipulation, unsafe firmware changes, and protocol misuse.
In 2025, half of OT attacks used weak remote access, according to reports. OT security tools look for unusual behavior that doesn’t match normal system activity. OT IDS IPS sensors monitor traffic at critical junctions without inline risk.
Vulnerability management ICS identifies exposed firmware, weak passwords, and unsupported operating systems.
OT ransomware defense keeps systems safe by finding threats early and stopping malware from spreading. Research from the SANS Institute emphasizes using passive detection to protect delicate devices.
Threat detection workflows usually include these steps:
This method prioritizes response based on operational consequence.
Bridging the IT and OT security gap means getting people, processes, and technology to work together. In 2025, attackers used this gap in 60% of incidents involving both IT and OT systems.
IT focuses on confidentiality and rapid patching, while OT prioritizes availability and safety. IT OT convergence requires shared governance, clear ownership, and unified monitoring. OT SIEM integration allows security teams to correlate IT alerts with OT events in one view.
Technology plays a supporting role. DMZs, one-way gateways, and data diodes keep systems safe while letting data be shared safely. Studies show that teamwork is just as important as the technology.
Successful gap bridging delivers practical outcomes:
Alignment reduces risk without slowing operations.
Choosing an OT security provider in California takes more than buying software; it means following the country’s toughest digital safety rules.
Beyond federal NERC CIP mandates, California operators must comply with SB 327, the state’s pioneering IoT security law.
This requires every “connected device”, from a smart actuator to a network gateway, to be equipped with unique authentication and “reasonable security features” at the point of sale.
California’s water sector is a primary example of security-as-an-enabler.
To remain resilient, California operators should:
“A manufacturer of a connected device shall equip the device with a reasonable security feature or features that are all of the following: (1) Appropriate to the nature and function of the device. (2) Appropriate to the information it may collect, contain, or transmit. (3) Designed to protect the device and any information contained therein from unauthorized access, destruction, use, modification, or disclosure.” – LegiScan [1].
OT security rules like NERC CIP make bulk electric system operators follow specific security steps. Non-compliance fines can exceed $1 million per day, making monitoring essential.
“EPAct 2005 provides that persons and organizations that violate a Reliability Standard are subject to civil penalties of up to $1 million per day per violation, helping to ensure reliability of the nation’s bulk power system.” – FERC.gov [2]
NERC CIP-002 requires operators to correctly identify and classify all parts of the bulk electric system (BES). CIP-005 enforces electronic security perimeters and access controls. CIP-007 addresses system security management, while CIP-008 mandates incident reporting within 24 hours.
In 2025, 58% of utilities were covered by NERC CIP rules, and 26% failed audits, according to regulators. The Federal Energy Regulatory Commission says that keeping an eye on systems and good records helps avoid audit problems.
The table below summarizes key NERC CIP controls supported by OT monitoring.
| NERC CIP Standard | Monitoring Contribution | Operational Benefit |
| CIP-002 | OT asset discovery and classification | Accurate BES scope |
| CIP-005 | Access monitoring and perimeter alerts | Reduced intrusion risk |
| CIP-007 | Vulnerability and configuration monitoring | System hardening |
| CIP-008 | Incident detection and reporting support | Faster compliance response |
Monitoring transforms compliance from periodic effort to continuous control.
ICS incident response planning shows how organizations deal with and fix OT cyber attacks. Plans must balance speed with safety.
In 2025, only 14% of organizations felt ready to handle OT incidents, even if they noticed them fast. When an ICS incident happens, the first step is to contain it using tools like air gaps or separate networks before fixing it.
A good plan also investigates the incident, looks at what went wrong, and plans recovery in a way that doesn’t disrupt normal operations.
ICS tabletop exercises conducted quarterly improve coordination between engineering, IT, and leadership. Guidance from the Cybersecurity and Infrastructure Security Agency emphasizes rehearsal over documentation alone.
A mature response program includes these components:
Preparation reduces downtime and recovery risk.
Protecting critical infrastructure security requires continuous monitoring, resilience planning, and cultural commitment. Ransomware affected 50% of organizations with OT environments in 2025, highlighting systemic risk.
Defense strategies include zero trust OT, role based access OT, and multi factor OT authentication where feasible.
Supply chain OT risks and third party OT access demand monitoring beyond the perimeter. OT training programs and awareness cybersecurity OT initiatives reduce human error.
Critical infrastructure operators increasingly align with national guidance. The Cybersecurity and Infrastructure Security Agency says being resilient means quickly finding problems, keeping systems separate, and having a plan to recover, not just preventing attacks.
Long-term protection blends technology and governance:
Resilience grows through steady, measurable progress.
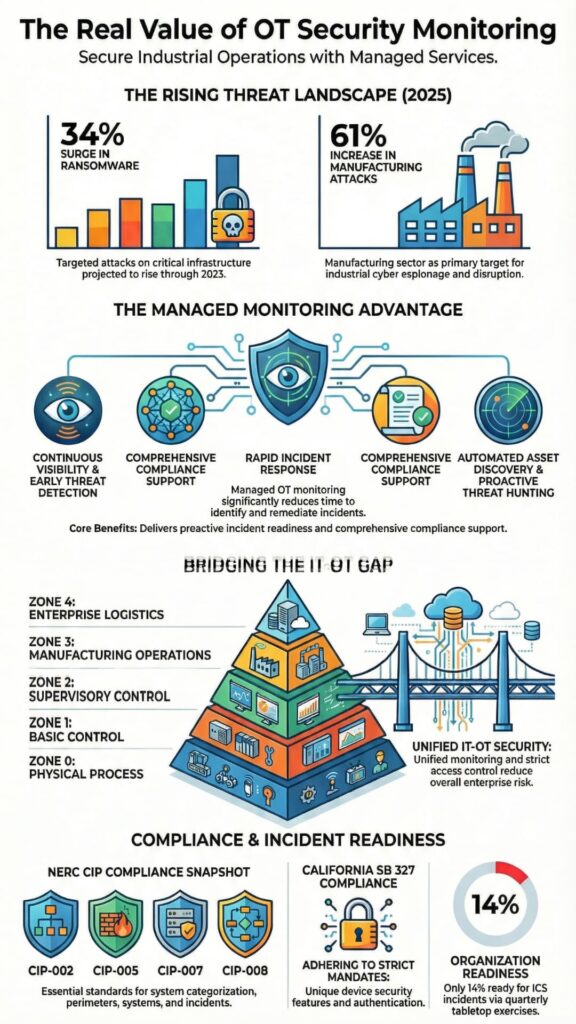
Purdue model security monitoring keeps industrial systems safe with several layers of security and helps follow the rules. It also organizes systems into zones, from physical processes up to enterprise systems.
Purdue level 0 security protects sensors and actuators. Level 1 controllers protection focuses on PLCs. Level 2 supervisory monitoring covers HMIs and SCADA, while level 3 MES security manages operations systems. Level 4 enterprise OT connects to IT networks through a DMZ OT IT zone.
Firewalls and zone segmentation ICS enforce conduits between levels. OT IDS IPS sensors at levels 2 and 3 monitor supervisory traffic.
In regulated sectors, unidirectional flows support compliance and safety. Industry guidance from ISA Secure reinforces Purdue as a practical framework for monitoring.
Purdue-based monitoring delivers structured control:
The model provides a shared language for engineers and security teams.
OT security monitoring protects industrial operations by continuously observing networks, devices, and system behavior. It detects operational technology threats, OT vulnerabilities, and abnormal activity early. This improves ICS security, strengthens OT network visibility, and reduces the risk of disruptions to safety, production, and regulatory compliance across critical infrastructure environments.
Managed OT services provide continuous OT SOC monitoring, OT threat detection, and OT anomaly detection without increasing internal workload.
They strengthen industrial control systems protection through OT asset discovery, vulnerability management ICS, OT forensics, and structured OT recovery planning. These services also support OT compliance auditing and reduce the risk of OT ransomware defense failures and cyber-physical attacks.
OT network visibility provides a complete view of devices, traffic flows, and system behavior across industrial control systems. Using OT traffic analysis, behavioral analytics OT, and deep packet inspection OT, teams detect OT disruption attacks faster.
This strengthens ICS incident response, supports OT SIEM integration, and improves manufacturing cybersecurity, energy sector OT, and water utility security programs.
IT OT convergence aligns security practices across business and operational networks. IT OT gap bridging improves OT cybersecurity by unifying monitoring, access control, and incident response. This supports network segmentation OT, zero trust OT, and OT firewall rules while reducing risks from insecure remote access OT security and unmanaged third party OT access.
OT security monitoring supports NERC CIP compliance by continuously tracking assets, access activity, and security events. It helps organizations meet CIP standards such as NERC CIP-002, CIP-005 access controls, CIP-007 system security, and CIP-008 incident reporting. This strengthens critical infrastructure security across the bulk electric system BES and improves long-term OT compliance auditing.
OT security monitoring keeps industrial systems safe, ensures compliance, and blocks threats. Using managed services, clear monitoring, and Purdue-style models protects ICS environments without slowing operations.
As attacks increase and regulations get stricter, monitoring becomes part of everyday operations, not just a reaction. Companies that act now can respond faster, pass audits more easily, and better protect critical systems.
Get expert guidance and optimize your security operations. We offer expert consulting tailored for MSSPs to streamline operations, reduce tool sprawl, and improve service quality. Our services include vendor-neutral product selection, auditing, stack optimization, and decision support.
With over 15 years of experience and 48K+ projects completed, we provide needs analysis, vendor shortlisting, PoC support, and clear recommendations, so you can build a tech stack that aligns with your business goals and operational maturity.
References
Related Articles