Address
304 North Cardinal St.
Dorchester Center, MA 02124
Work Hours
Monday to Friday: 7AM - 7PM
Weekend: 10AM - 5PM
Address
304 North Cardinal St.
Dorchester Center, MA 02124
Work Hours
Monday to Friday: 7AM - 7PM
Weekend: 10AM - 5PM
Host Based Intrusion Detection (hids) act like digital security cameras inside computers and servers. They scan system files, logs, and user behaviors to catch malware and hackers that sneak past firewalls. While network security tools watch traffic between machines, HIDS focuses on catching threats already inside a single device.
Think of HIDS as a guard dog that knows exactly what belongs in your house – it barks at unfamiliar changes to important files, weird program behavior, or suspicious user activities. Many organizations pair HIDS with other security tools to build stronger defenses.
Want to see real examples of HIDS catching threats? Keep reading for eye-opening cases and setup tips.
Picture a digital security guard posted inside every computer. HIDS tools watch the machine’s vital signs – logs, files, processes, registry tweaks. While network scanning catches bad guys at the gates, HIDS spots the ones who snuck past security.
Working with MSSPs since 2019, we’ve seen these systems evolve from basic file checkers to smart threat hunters. Just last week, one caught a nasty rootkit trying to hide in a client’s system files. The network tools? Completely missed it. That’s exactly why layered security isn’t just consultant-speak.
Most security teams run HIDS as their ground-level defense. After deploying it across hundreds of client networks, we know it catches what perimeter security misses. [1]
There’s three main parts (trust me, we’ve tried every setup imaginable):
Look, every network’s different.
Cookie-cutter solutions often miss the mark. That’s why MSSPs rely on us to tailor each deployment. [2]
Credit: UnitedLayer
HIDS runs continuously, analyzing system events as they happen. This real-time vigilance allows early detection of intrusions, often before damage spreads. It watches for:
We see that this detailed monitoring is crucial, especially in places with insider threats or targeted attacks.
Early Threat Detection and Response: HIDS runs directly on your device. It finds problems early, sometimes before hackers can spread. This lets security teams act quickly and stop attacks before they worsen.
Better Visibility: HIDS shows what’s really happening in your system. It can spot changes to files, new programs, and unusual user behavior that network tools might miss.
More Accurate Alerts: HIDS finds threats in different ways, cutting down on false alarms through reducing false positive IDS alerts techniques. This helps security teams focus on real issues instead of harmless alerts.
Helps with Compliance: Regulations like HIPAA and PCI DSS need constant monitoring of key systems. HIDS makes compliance easier by tracking and reporting any changes.
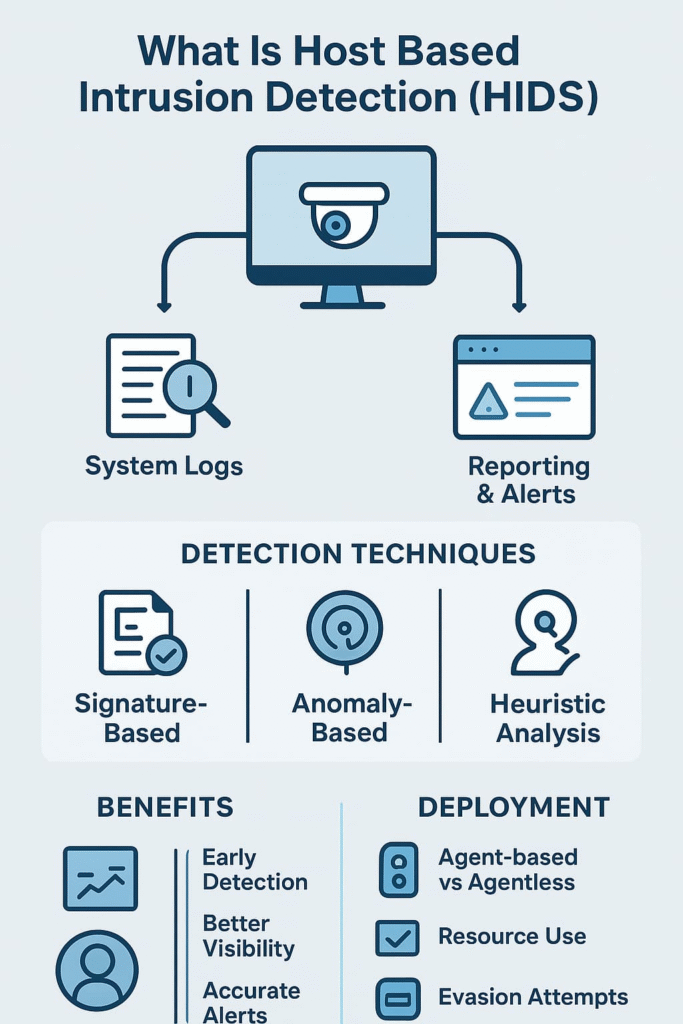
Choosing a HIDS depends on factors like:
Agent-based HIDS provide deep host visibility but consume more resources. Agentless options are lighter but might miss certain data points. We’ve learned that balancing these trade-offs depends heavily on your environment’s size and critical assets.
Many MSSPs rely on expert guidance when choosing a managed IDS/IPS vendor to ensure their tools offer flexibility, sensor management, and integration that suits their evolving networks.
HIDS doesn’t work in isolation.
It complements antivirus, firewalls, and network IDS by covering their gaps. Feeding HIDS alerts into SIEM platforms offers unified visibility. This makes it easier to link suspicious activities across the network and hosts.
This integrated visibility and management are key for effective intrusion detection system management, providing real-time threat detection and response across the security stack.
In our experience, this layered approach greatly boosts security and speeds up threat hunting and incident response.

Despite these challenges, HIDS remains a crucial tool when combined with other defenses. Proper management and regular updates are key to maintaining its effectiveness.
A host-based intrusion detection system watches what happens inside a computer or server. The HIDS system tracks system calls, log analysis, file integrity monitoring, and user activity monitoring to find suspicious changes. It helps catch malware detection, insider threat detection, and unauthorized access detection before bigger damage happens.
Anomaly detection studies normal host behavior and flags odd actions, while signature-based detection looks for known intrusion signatures. A good host IDS often combines both methods.
This helps reduce false positives and makes behavior-based detection stronger against zero-day attack detection and advanced persistent threat detection.
File integrity monitoring helps spot unauthorized change detection on important system files. By comparing files against trusted versions, it alerts teams when something suspicious happens.
This part of endpoint security works with process monitoring, registry monitoring, and kernel-level monitoring to stop rootkit detection issues and maintain system integrity verification.
Many businesses use HIDS for compliance monitoring with rules like HIPAA security or PCI DSS compliance. HIDS collects auditd logs, system audit logs, and syslog monitoring data. With security event correlation and SIEM integration, it provides security reporting that proves systems meet endpoint compliance and proper configuration auditing standards.
To sum up, Host-Based Intrusion Detection Systems act as the eyes and ears inside your endpoints. They deliver the deep visibility and early warnings needed to defend against today’s advanced cyber threats. When deployed and managed effectively, HIDS becomes a critical part of any strong cybersecurity strategy.
Join our expert MSSP consulting program to streamline your operations, reduce tool sprawl, and strengthen your cybersecurity stack with guidance from seasoned professionals.