Address
304 North Cardinal St.
Dorchester Center, MA 02124
Work Hours
Monday to Friday: 7AM - 7PM
Weekend: 10AM - 5PM
Address
304 North Cardinal St.
Dorchester Center, MA 02124
Work Hours
Monday to Friday: 7AM - 7PM
Weekend: 10AM - 5PM
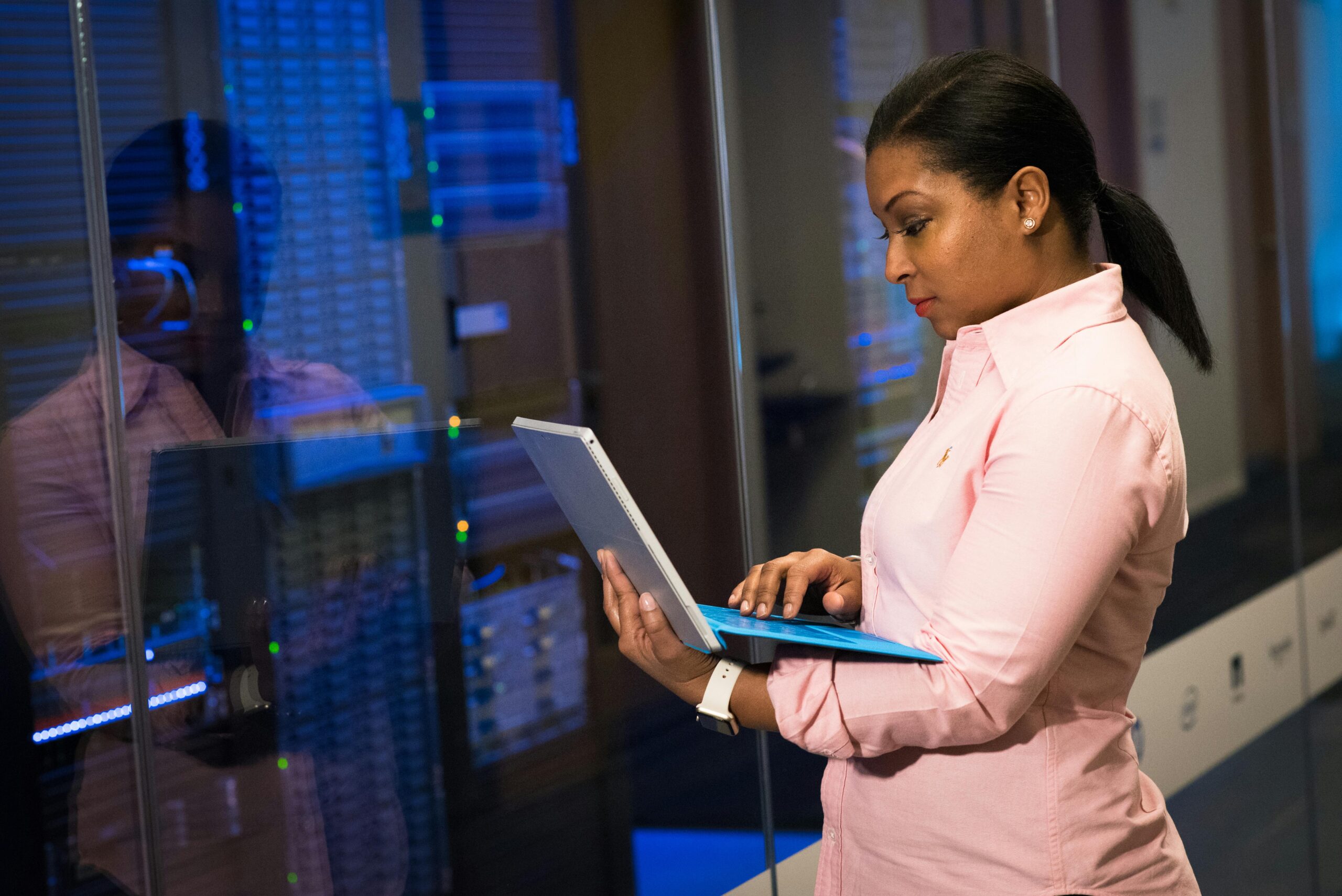

Security scanning doesn’t cut it anymore , that’s just facts. Companies need dedicated pros watching their networks round clock, not just running occasional checks. These specialists (armed with a mix of AI tools and years of field experience) catch weird patterns and potential threats before they turn into full, blown disasters.
Even solid in-house teams struggle keeping up with the endless stream of new vulnerabilities. It’s not their fault , there’s just too much ground to cover. That’s why businesses are quietly shifting to managed security teams who handle the heavy lifting. Want to know what makes these teams tick? Keep reading.
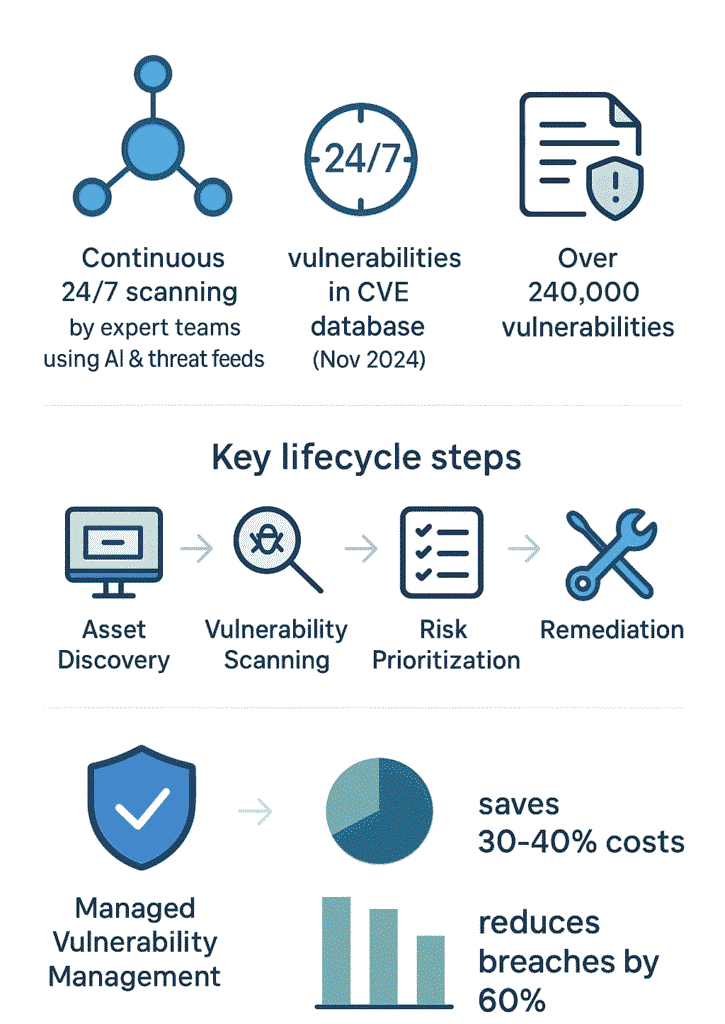
Walking through any decent,sized company’s IT department these days, you’ll notice something’s changed. More and more businesses are shipping their security headaches to the pros , people who’ve spent years in the trenches dealing with cyber threats.
These security teams (usually scattered across different time zones) work round the clock, poking and prodding at networks to spot trouble before it hits.
They’re checking everything from ancient Windows servers that nobody wants to touch, to those fancy cloud systems everyone’s so proud of. It’s kind of like having an obsessive security guard who never takes lunch breaks.
Adding to that, as of November 2024, there are over 240,000 vulnerabilities catalogued in the CVE database, underscoring the sheer scale of what needs to be monitored and managed (1)
Security’s gotten complicated , way more than just installing some antivirus and calling it a day. Here’s what these teams actually do:
Most of these teams plug into some pretty serious threat feeds (some tracking thousands of new threats every hour), and they’re always watching for the next big problem. Plus, they write up these detailed reports that keep the suits happy and the auditors off everyone’s back.
The whole thing works like this:

Credit: pexels.com (Photo by Tranmautritam)
The do it yourself approach to vulnerability management isn’t pretty. Companies end up with their IT teams stretched thin, running scans between meetings and hoping they don’t miss anything critical.
A typical 500-person company might spend 40+ hours weekly just keeping up with new threats, and that’s if they’re lucky. The security staff ends up playing catch-up most days, scanning systems whenever they can squeeze it in.
Forbes reports that 62% of organizations knowingly ship insecure code, and nearly 80% of security leaders express deep concern that a breach could result in severe consequences (2).
Going solo means playing a guessing game with risk levels. Teams might patch everything they find, wasting time on low-risk issues, or worse miss the scary stuff hiding in plain sight.
It’s like trying to find a needle in a haystack, except the needle might crash your entire network. Most companies patch about 60% of their vulnerabilities within 90 days, but they’re probably not fixing the right ones first.
The lack of 24/7 monitoring leaves gaps you could drive a truck through. New vulnerabilities pop up daily, and without constant attention, they’ll pile up fast, which is why having a clear vulnerability assessment process is essential.

Credit: pexels.com (Photo by Christina Morillo)
Professional scanning runs like clockwork; there’s no “we’ll get to it next week” attitude. These guys run scans every 24 hours on average, sometimes more for critical systems.
They’re checking everything from the company website to Bob’s laptop in accounting, and they’re doing it with tools that cost more than a year’s salary.
Here’s where the pros earn their keep. They don’t just look at CVSS scores (those 1-to-10 ratings that tell you how bad a vulnerability is), they’re mixing in real world attack data, asset values, and yeah sometimes what the hackers are talking about on the dark web.
A good provider might identify 30% fewer “critical” vulnerabilities than automated tools alone, but they’re the ones that actually matter.
Fixing holes isn’t just about downloading patches. These teams coordinate with IT departments like orchestra conductors, scheduling fixes around business hours and critical operations.
They’ll track every patch, retest systems, and yeah sometimes they’ll bring in hackers (the good kind) to make sure everything’s actually fixed.
Nobody likes paperwork, but these reports keep auditors happy and executives informed. Monthly reports might run 50+ pages, breaking down everything from patch success rates to risk trends.
And when the auditors come knocking (they always do), there’s a paper trail a mile long showing exactly what’s been done.
Nobody wants to admit it, but most companies don’t have the tools to catch every security hole. Working with outside experts (who’ve probably seen every hack attempt imaginable) means finding problems faster and fixing them before they turn into disasters.
They’ve got access to tools that cost more than most IT budgets, and they know exactly where to look.
Think of it like closing windows in a house, the fewer open spots, the harder it is for thieves to break in. These teams work round the clock checking for weak spots, and their track record shows about 60% fewer successful attacks compared to companies going it alone.
The security world changes every day, sometimes every hour. These management teams plug into threat feeds that cost anywhere from $50,000 to $200,000 annually, catching new threats as they pop up. They’re usually 48,72 hours ahead of the news cycle on major vulnerabilities.
Let’s face it, IT teams are stretched thin enough already. When someone else handles the day,to,day security scans, the regular staff can actually focus on bigger projects instead of putting out fires all day.
Most companies can’t find (or keep) good security people , there’s about 3.5 million unfilled cybersecurity jobs worldwide right now. Managed services fill that gap without the headache of hiring.
Companies grow, networks get messier, and suddenly there’s twice as much to protect. These services grow with you, whether you’ve got 100 endpoints or 10,000.
Running security in,house isn’t cheap , figure $150,000+ yearly for a decent setup. Managed services usually run 30-40% less, and you don’t have to worry about training or tools.
Not everyone’s a security expert, and they don’t need to be. These services break down complex problems into plain English and clear action items.
They’ll keep the paperwork straight, which matters when auditors come knocking. Most services maintain documentation that meets standards like SOC 2, ISO 27001, and HIPAA without extra work from your team.
Nothing’s worse than picking the wrong security provider, it’s like hiring a locksmith who can’t tell a deadbolt from a doorknob. When choosing someone to manage vulnerabilities, they’ve got to know their stuff, have the right tools, and actually pick up the phone when there’s trouble.
The provider’s got to run modern scanning tools (ones from this decade, at least) and know how to use them. If they can’t explain their threat intel sources or don’t know your tech setup, that’s a red flag.
Support teams that ghost you when systems are down? No thanks. Get everything in writing , response times, escalation paths, the works.
Some providers want to take over everything, others work alongside your team. Pick what matches your setup and budget.
The big players stand out by actually using automation correctly, having real threat intel (not just repackaged news), and knowing your industry’s quirks.
It shouldn’t take an act of Congress to get the provider’s tools working with yours. If they can’t play nice with your current setup, move on.
Strong setups also align with EDR solution deployments, ensuring endpoint protection meshes seamlessly with vulnerability tracking.
Your provider needs to handle whatever you’re running , old school data centers, cloud stuff, or both. No exceptions.
Speed matters here. Good automation catches problems fast and tells the right people. Even better if it works with your other security tools.
Threats change, your business changes, the provider better keep up. They should be updating their stuff regularly, not running last year’s playbook.
Just because something’s fixed doesn’t mean it stays fixed. Smart providers check their work and keep an eye out for new problems.
When new threats pop up, plans need to change. The provider should adjust fixes based on what’s actually dangerous right now, not what was scary six months ago.
Most security teams need consistent updates, that’s just basic common sense. Reports can range from quick,hit bullet points (perfect for busy C,suite types who just want the big picture) all the way to 50 page technical deep dives that engineers actually read.
The best providers let teams pick what works for them, no one size fits all nonsense here.
Nothing messes up security faster than mixed signals between teams. Good communication means having a playbook everyone follows, who gets called when something breaks, which Slack channel to use, and who’s got final say on fixes. Simple stuff that makes a huge difference.
Security programs need to grow with the company, period. When IT adds 100 new servers or shifts half the infrastructure to the cloud, the scanning and monitoring better keep up without missing a beat. No excuses.
Not every system needs the same treatment. Web servers might need daily scans while that old printer in accounting (you know the one) probably doesn’t. Smart providers get this and adjust their approach accordingly , scanning frequencies, detection methods, the whole nine yards.
Managed vulnerability management isn’t just about outsourcing scan duties,it’s about trusting security specialists who keep constant watch over your digital assets. With the right team in place, your staff can finally breathe easier, no longer tied to dashboards around the clock.
These experts know where to find real threats and make sure you’re meeting compliance requirements. And with cyberattacks evolving rapidly, some reports suggest new threats emerge every 39 seconds.
For organizations that don’t want to build a full in-house security team or wrestle with complicated tools, leveraging outside experts just makes sense.
Join us today and let our 15+ years of experience, 48K+ completed projects, and proven consulting expertise help streamline operations, reduce tool sprawl, and strengthen your defenses.
From needs analysis and vendor shortlisting to PoC support and actionable recommendations, we’ll guide you in building a security stack that aligns with your business goals and operational maturity.
Managed vulnerability management goes beyond a typical vulnerability management service by adding expert support, guidance, and ongoing oversight. Instead of only offering tools, it covers the vulnerability management process from asset discovery to vulnerability identification and remediation.
The vulnerability lifecycle shapes how a vulnerability management program operates. It starts with vulnerability discovery and vulnerability identification, moves through vulnerability prioritization, and ends with vulnerability remediation and vulnerability mitigation.
Vulnerability scanning detects weaknesses, while continuous vulnerability monitoring tracks them over time. Together, they support the vulnerability management workflow by feeding data into vulnerability assessment and vulnerability analysis.
Risk-based vulnerability management uses vulnerability intelligence, vulnerability classification, and vulnerability risk assessment to decide which threats matter most. Vulnerability prioritization and vulnerability triage.