Address
304 North Cardinal St.
Dorchester Center, MA 02124
Work Hours
Monday to Friday: 7AM - 7PM
Weekend: 10AM - 5PM
Address
304 North Cardinal St.
Dorchester Center, MA 02124
Work Hours
Monday to Friday: 7AM - 7PM
Weekend: 10AM - 5PM

Staring at screens all night isn’t practical, but endpoint security does that job for IT teams. Like a digital night watchman, it keeps tabs on every device that’s linked to company networks, from Bob’s work laptop to those new smart thermostats in the break room.
The timing makes sense. Most hackers hit between 2 and 4 AM, probably thinking they’re being sneaky while everyone’s asleep. But with 24/7 monitoring, the security team gets alerts within minutes, not during Monday’s damage control meeting.
Want to know what else endpoint security catches while you sleep? Keep reading.
Not a single endpoint sits idle these days. From the moment a device powers on till it shuts down, there’s someone (or something) trying to break in.
Every device needs constant eyes on it , that’s just how it is now. When organizations miss monitoring even one device, it’s like leaving the back door unlocked. A network’s only as strong as its weakest endpoint.
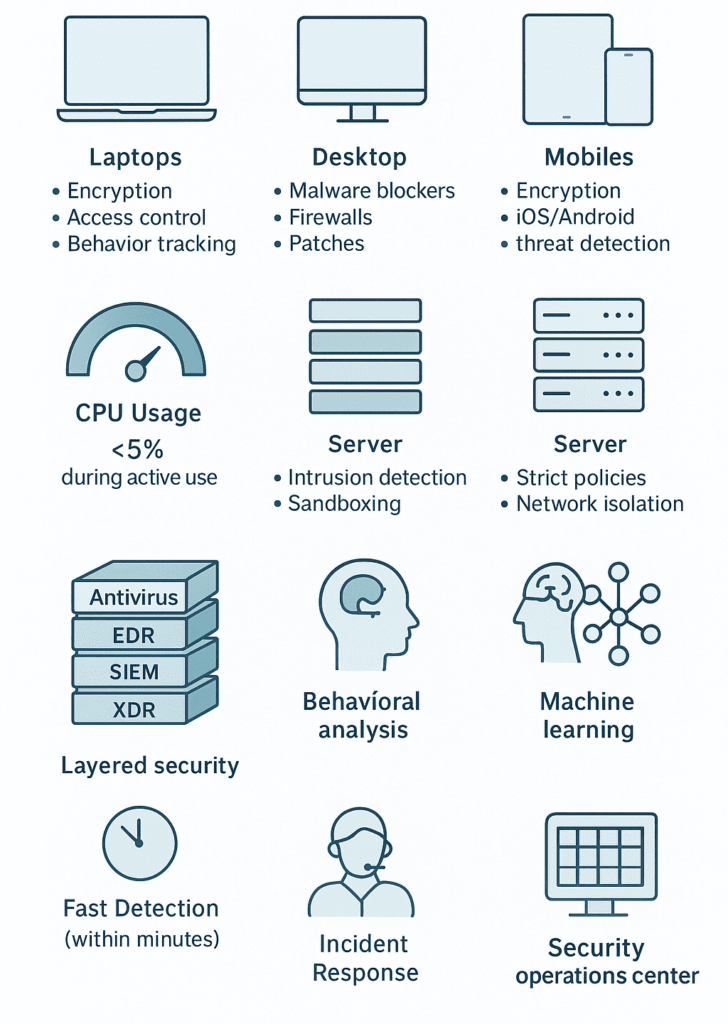
Each piece of hardware needs its own security approach, cause let’s face it, a laptop doesn’t face the same risks as a printer.
According to IBM, up to 90% of successful cyberattacks and 70% of data breaches originate from endpoint devices such as laptops, mobile phones, and IoT gadgets (1)
These days laptops bounce between coffee shops, home offices, and God knows where else. They need serious protection.
Encryption that locks down data tight, strict access controls (no more password sharing), and behavior tracking that spots when something’s off. Like when accounting suddenly starts accessing files at 3 AM.
Sure, desktops don’t move around, but they’re still prime targets. They need solid malware blockers and firewalls that actually work. Regular patches (at least every 14 days) keep the zero day hunters at bay.
Phones and tablets are basically pocket sized computers now. They need specialized security , strong encryption and threat detection built for iOS and Android. Cause when someone loses their phone at a bar, that’s a potential data breach walking out the door.
Servers are the crown jewels, holding everything from customer data to the entire business operation. They need hardcore intrusion detection and sandboxing that isolates anything suspicious. One wrong move here could take down the whole company.
These things are everywhere now , cameras, sensors, even smart coffee makers. Problem is, most ships have security that’s barely there. They need strict policies and regular checkups, plus isolation so one compromised thermostat can’t bring down the network.
The challenge isn’t just watching everything , it’s doing it without grinding work to a halt. Security that slows down devices is security that gets turned off.
There’s no clocking out in security. Modern EDR systems paired with XDR platforms (think of them as security cameras that never blink) keep watch 24/7.
Nobody’s got time for security that turns their computer into a slug. The best tools use AI to adjust their scanning intensity , heavy when the device is idle, lighter when someone’s trying to get work done. Most aim to stay under 5% CPU usage during active hours.

Credit: pexels.com (Photo by cottonbro studio)
From the trenches of endpoint defense, an uneasy truth emerges: security tools, on their own, might miss critical threats. But combine them right, and they’ll catch most attackers before real damage hits.
Think of endpoint security like layers of an onion , each one adding protection, each one working a bit differently. One tool’s weakness gets covered by another’s strength.
First line of defense, stops known malware using signature-based scanning combined with heuristic detection. Enhancements now include behavior-based analysis and machine learning for proactive threat detection (2)
EDR systems collect the little things that matter, like when someone logs in at 3 AM or when files start encrypting themselves. They’ll watch, record, and (when needed) wake up the security team.
Old school antivirus isn’t dead yet. It’s still catching the everyday threats, scanning files in milliseconds (usually under 100ms), checking them against known bad stuff. But the real value comes when organizations look at EDR vs antivirus, since layering them closes gaps that either tool might miss alone.
SIEMs connect the dots between what’s happening on laptops, servers, and networks. They’re like security cameras that can see everything at once, picking up patterns humans might miss.
XDR takes that endpoint view and stretches it wider , way wider. Cloud apps, network traffic, user behavior , it’s all fair game for these systems.
Security teams can’t just sit back and wait anymore , cyber threats keep getting nastier. They’ve had to get creative with their methods, building up some pretty sophisticated ways to catch bad guys. Here’s what’s working right now:
The best threat detection in the world doesn’t mean much if you don’t know what to do when you catch something. Here’s how teams handle it:
All these pieces work together, kind of like a digital immune system. It’s not perfect, but it’s getting better all the time, and that’s what matters in this constant game of digital cat and mouse.
The basic truth about signature detection? It’s like a security guard with a most wanted list, checking faces against photos. Simple but limited.
Points worth noting:
Known Threats
The Big Problem
Moving Beyond the Basics
Between updates and behavior tracking, security’s getting better at catching the new stuff. But here’s the kicker , signature detection still matters. It’s just not enough by itself anymore. Sort of like bringing just a shield to a modern battlefield , you’re gonna need more tools in that arsenal.

Credit : pexels.com (Photo by Antoni Shkraba Studio)
No system’s truly secure without the right people watching the screens around the clock.
Years of observations from SOC floors show that you can’t beat the combo of sharp analysts and smart automation. Like a well,oiled machine, each part’s got to work just right.
These folks don’t just stare at screens all day , they’re digging through incidents, tweaking those detection rules (sometimes they’re too sensitive, sometimes not enough), and making sure every alert that goes up the chain matters.
Many businesses lean on managed EDR setups here, so security teams can scale oversight without burning out their in-house staff.
Security operations never sleep, and that’s where automated systems come in. They’re the digital workhorses that keep an eye on things while everyone else is dreaming.
These systems handle the grunt work, sifting through mountains of alerts (sometimes up to 10,000 per day) so the experts can tackle the real problems.
Think of automated systems as the first line of defense in a security team’s arsenal. They’re like having extra sets of eyes constantly scanning for trouble, but without the human tendency to get bleary,eyed at 3 AM.
The machines follow pre-set rules and playbooks, making split,second decisions that would take people much longer to process.
The sun might set, but security threats don’t clock out at 5 PM. These systems keep running through holidays, weekends, and those long hours when most folks are sleeping. Security analysts work in rotating shifts, typically 8-12 hours each, but the automated systems never take breaks or call in sick.
Every second counts when there’s a security breach. That’s where SLAs come in, they’re the promises made to clients about response times. The automated systems help security teams hit these targets, processing about 85% of routine alerts without human intervention.
The clock starts ticking the moment something suspicious happens. Five minutes to spot it, thirty minutes to respond , those aren’t just random numbers. They’re based on how fast threats can spread (a ransomware can encrypt 10,000 files in under 10 minutes).
One screen to rule them all , that’s what centralized visibility means for security teams. They can monitor anywhere from 5,000 to 50,000 devices at once, catching weird behavior patterns that might signal trouble. No more switching between dozens of different tools.
Ever wonder what’s really happening when your computer acts weird? There’s probably more going on than meets the eye.
The average computer faces about 2.5 million cyber threats per second (that’s not a typo). Here’s what’s usually trying to get in:
When it comes to catching these threats, timing is everything. Most successful attacks only need about 98 minutes to get what they want.
When organizations understand these threats and how to spot them, they’ve got a fighting chance at keeping their data safe. No guarantees though , cybersecurity’s a bit like trying to patch holes in a boat while sailing through a storm.
It’s fascinating how modern businesses can’t escape the web of security rules that protect our digital lives. Our team’s seen plenty of companies scrambling to get their security right.
There’s a world of rules and regulations that companies can’t escape these days. Not just suggestions scribbled on paper, but real, teeth,clenching requirements that pack serious consequences if ignored. Every piece of data needs protection, like a precious family heirloom that can’t be replaced.
It’s pretty straightforward , computers, phones, tablets, anything connected to your company needs constant monitoring. No shortcuts allowed.
These aren’t your grandmother’s guidelines from the early days of computing, they’re hardcore requirements with real teeth behind them. Miss a step, and you might find yourself explaining to a board why your company’s name is splashed across headlines.
Hospitals face some of the toughest standards around (and for good reason). Every keystroke, mouse click, and file access needs tracking , kind of like having a security camera pointed at your data 24/7.
Medical staff can’t just wander through patient files anymore, they need proper clearance and documentation for every peek at someone’s records.
Europe doesn’t mess around with privacy. Their rules hit like a hammer , 72 hours to report problems, no exceptions. Companies scramble to keep up with GDPR’s demands, because of those fines? They’ll make your accountant cry. It’s about treating personal data like it’s worth its weight in gold.
Money talks, and so do hackers. That’s why payment systems need bulletproof protection (or as close as we can get). Every computer touching credit card info needs serious encryption , think military,grade scrambling that would give code breakers headaches.
Think of ISO 27001 as the honor roll of information security. Companies can’t just say they’re secure, they’ve got to prove it with mountains of documentation and constant vigilance. It’s like getting a black belt in data protection, but the training never stops.
Security isn’t a set,it,and,forget,it deals. It needs daily attention, like a garden that’ll wilt without care. Staff training, regular updates, constant monitoring , it’s all part of the package. Miss one day, and things could start falling apart.
Every click, every login, every file transfer needs recording. These digital footprints might seem excessive, but they’re gold when something goes wrong. Companies need these records like a lifeline, ready to pull them out when auditors come knocking.
Just like you’d check your car’s engine regularly, systems need their own inspections. These audits aren’t just bureaucratic box ticking, they’re your early warning system for trouble ahead. Miss something small today, face something huge tomorrow.
Security teams can’t take their eyes off the ball. One slip up could mean trouble with regulators (and probably some hefty fines).
That’s where solid EDR management makes a difference, ensuring continuous monitoring and aligning day-to-day defense with compliance demands.
We’ve learned that endpoint security monitoring 24/7 isn’t just a nice-to-have. It’s the backbone of a strong cybersecurity strategy. If your team isn’t watching all endpoints all the time, you’re leaving the door open. Start by assessing endpoint device types in your environment and ensuring coverage for each.
Invest in layered endpoint security tools combining EDR, behavioral analytics, and automated response. Don’t forget the human factor,SOC analysts and clear SLAs make a huge difference.
If you want to keep your enterprise safe, consider how continuous endpoint monitoring fits into your broader security operations. It’s a long game, but one that pays off in fewer breaches, faster incident containment, and compliance peace of mind. Stay vigilant, stay protected, partner with us today.
Endpoint threat detection spots suspicious behavior, while real-time endpoint monitoring and continuous endpoint monitoring track activity as it happens. Together, they provide early warnings, close blind spots, and help stop problems before they spread.
Managed endpoint security usually involves outside experts to oversee devices. Endpoint detection and response (EDR) focuses on finding and reacting to threats on endpoints. Extended detection and response (XDR) goes further by combining data from networks, apps, and cloud systems for a wider view.
EDR solutions and endpoint protection software use behavioral analytics endpoints to detect unusual activity. Once flagged, automated incident response can isolate or fix issues within seconds, reducing damage and keeping devices safe without delay.
Ransomware protection endpoints are stronger when paired with endpoint vulnerability assessment and endpoint risk management. Vulnerability assessments find system gaps, while risk management decides which gaps matter most. Together, they reduce the chances of a ransomware attack.